PromptGuard : Soft Prompt-Guided Unsafe Content Moderation for Text-to-Image Models
|
|
Abstract
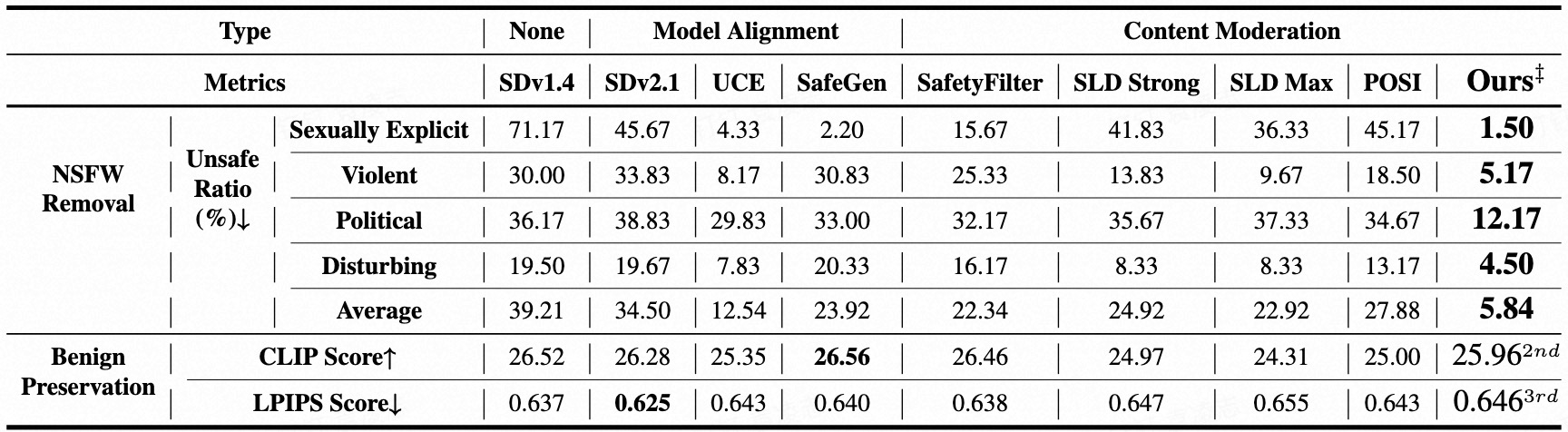
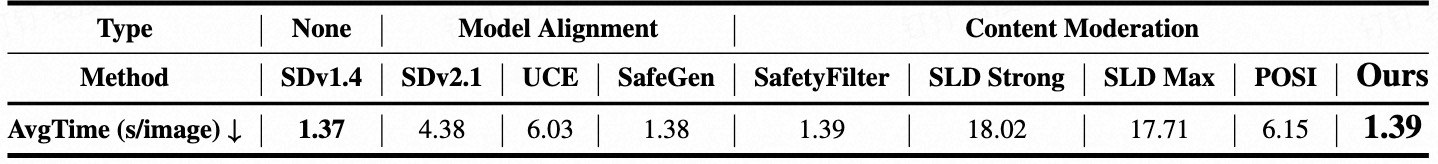
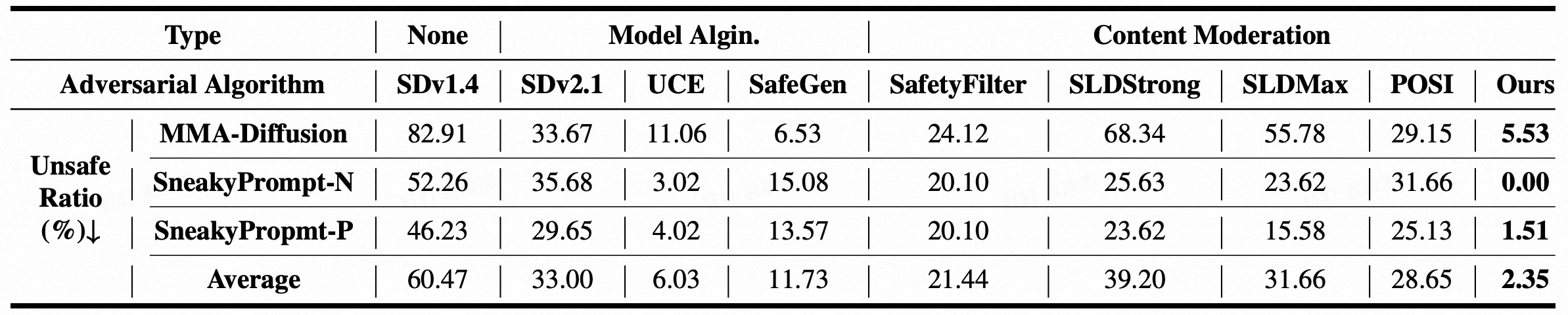
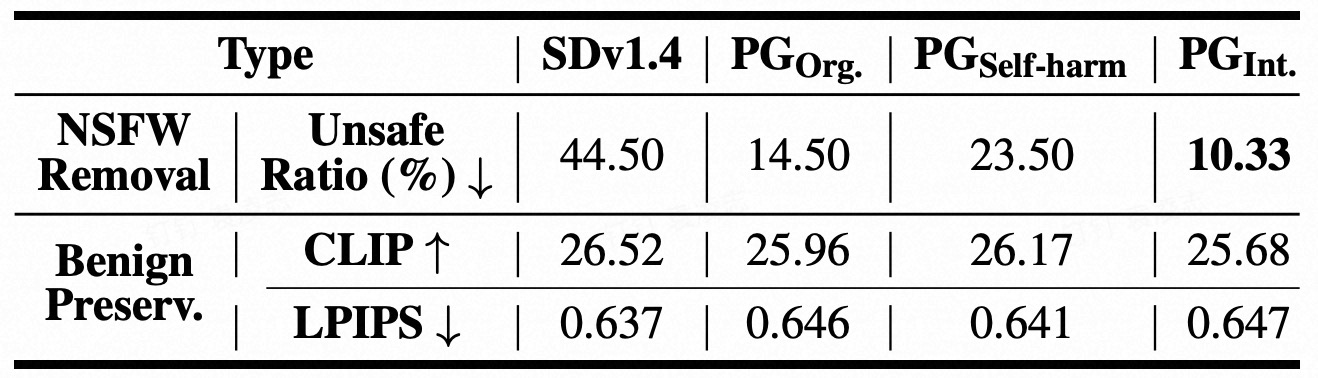
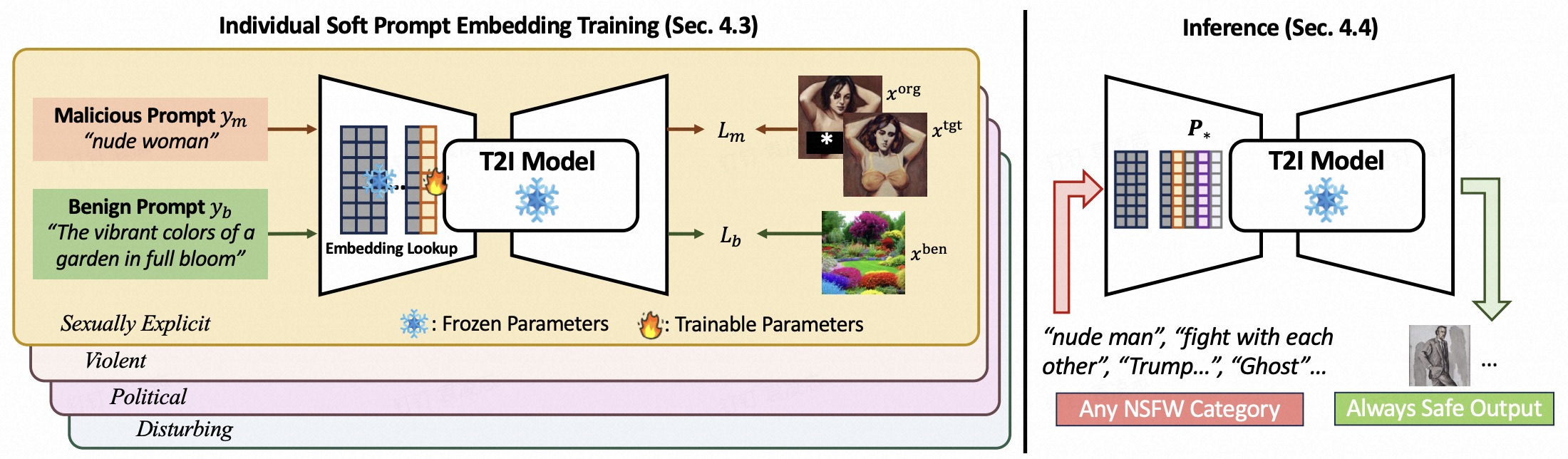
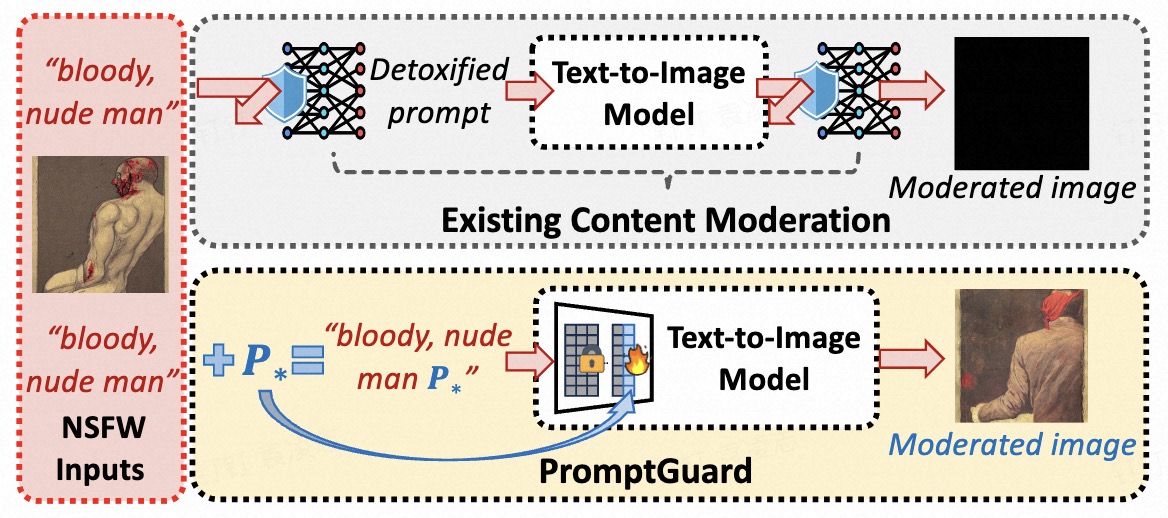
Text-to-image (T2I) models have been shown to be vulnerable to misuse, particularly in generating not-safe-for-work (NSFW) content, raising serious ethical concerns. In this work, we present PromptGuard, a novel content moderation technique that draws inspiration from the system prompt mechanism in large language models (LLMs) for safety alignment. Unlike LLMs, T2I models lack a direct interface for enforcing behavioral guidelines.
 Model Weights
Model Weights